HTTP JSON Sensor Data: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Zur Navigation springen
Zur Suche springen
Mb (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
Mb (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| Zeile 32: | Zeile 32: | ||
{"name": "Voltage", "unit": "V", "decPrecision": 3}, | {"name": "Voltage", "unit": "V", "decPrecision": 3}, | ||
{"name": "Current", "unit": "A", "decPrecision": 1} | {"name": "Current", "unit": "A", "decPrecision": 1} | ||
| − | ] | + | ], |
"properties": [ | "properties": [ | ||
{ "id": "L1", "name": "Meter1", "state": 1}, | { "id": "L1", "name": "Meter1", "state": 1}, | ||
| Zeile 44: | Zeile 44: | ||
{"name": "Temperature", "unit": "C", "decPrecision": 1}, | {"name": "Temperature", "unit": "C", "decPrecision": 1}, | ||
{"name": "Humidity", "unit": "%", "decPrecision": 1} | {"name": "Humidity", "unit": "%", "decPrecision": 1} | ||
| − | ] | + | ], |
"properties": [ | "properties": [ | ||
{ "id": "6102", "name": "Server-Rack", "state": 1} | { "id": "6102", "name": "Server-Rack", "state": 1} | ||
Version vom 1. April 2021, 14:34 Uhr
Preface
- all Sensor data is available in a generic JSON Object, presented by status.json
- there are two relevant sub-objects: sensor_values and sensor_descr
- sensor_descr can tell
- what sensor types are actually relevant
- what is the sensor type specific field description
- how many sensors of each type are actually present
- what are the names of each of those sensors
- sensor_values carries all measured sensor values, matching the description explained above, in the same order
- it's common practice to get sensor_descr+sensor_values once, and poll sensor_values only subsequently with much less payload
This empowers you to write small code supporting all products and all sensors in one single future-proof approach, without the need for sensor specific knowledge.
So your software is already prepared for new gude-devices, and prepared for new sensor Add-Ons.
To give an example, this documentation will highly depend on check_gude.py, our HTTP sensor data swiss-knife tool.
Getting Data
- HTTP-Get status.json?components=8470528
- for more info about status.json components flags, refer to EPC HTTP Interface
- 8470528 sums up sensor_values (16384 aka 0x10000) plus sensor_descr (65536 aka 0x4000), plus the ‘extended’ marker (0x800000) to get both simple sensors and (more complex) sensor groups
- 8470528 = 0x814000 = 0x4000 + 0x10000 + 0x800000
Example Data
sensor_descr
[
{
"type": 664,
"num": 2,
"fields": [
{"name": "Voltage", "unit": "V", "decPrecision": 3},
{"name": "Current", "unit": "A", "decPrecision": 1}
],
"properties": [
{ "id": "L1", "name": "Meter1", "state": 1},
{ "id": "L2", "name": "Meter2", "state": 1}
]
},
{
"type": 665,
"num": 1,
"fields": [
{"name": "Temperature", "unit": "C", "decPrecision": 1},
{"name": "Humidity", "unit": "%", "decPrecision": 1}
],
"properties": [
{ "id": "6102", "name": "Server-Rack", "state": 1}
]
}
]
This tells you:
- there a two Sensors of Type 664, and one of type 665
- a type-664 sensor has two Fields, Voltage and Ampere
- Voltage is measured with a decimal precision of 3, Ampere with a decimal precision of 1
- The two Type-664 sensors (L1 and L2) are named 'Meter1' and 'Meter2'
- The Type-665 Sensor is named 'Sever-Rack'
sensor_values
[
{
"type": 664,
"num": 2,
"values": [
[{"v": 233.19}, {"v": 3.2}],
[{"v": 226.2}, {"v": 0.3}]
]
},
{
"type": 665,
"num": 1,
"values": [
[{"v": 27.1}, {"v": 40.3}]
]
}
]
sensor_desc / sensor_values
bringing together this tells you:
L1/Meter1 233.19 V (Voltage), 3.2 A (Ampere) L2/Meter2 226.20 V (Voltage), 0.3 A (Ampere) 6102/Server-Rack: 27.1 C (Temperature), 40.3 % (Humidity)
Common Sensor Type IDs
1 Line power meter 9 Line power meter with residual Current 8 Outlet power meter 7 Digital Inputs 20 System Data (sensor group) 51 Temperature Sensor 52 Temperature/Humidity Sensor 53 Temperature/Humidity/AirPressure Sensor 101 Bank (eFuses Port-groups) Sensor (e.g. used at 8291 PDUs) 102 (DC) Power Sources
check_gude.py in action
- check_gude.py is a demo code to show how sensor_descr and sensor_values can be assembled generically to make use of all our devices / sensors
- so when new devices and sensors are coming up, check_gude.py is already prepared to deal with it
- install python along with requests to run check_gude.py
- feel free to use check_gude.py as you need it and to rewrite the given code to any language desired
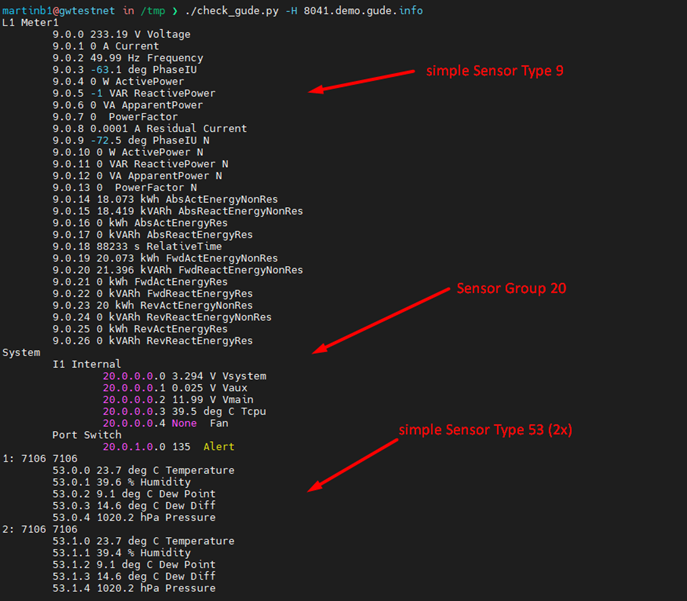
Show all Sensor Data
- Here a device with hostname 8041.demo.gude.info is queried to dump all sensor data
- with check_gude.py can use --ssl / --username / --password to benefit from HTTP encryption and user authentification
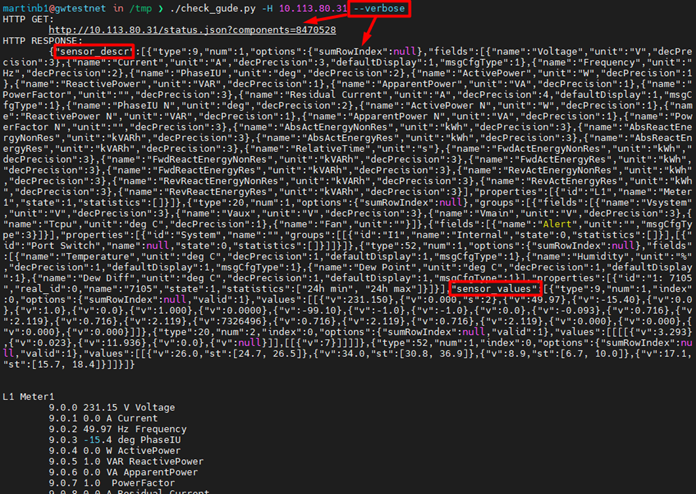
show CGI-Get / JSON Data
when using --verbose check_gude.py will print out the full URL and the JSON return data:
Sensor Groups
a simple sensor has one single field description, where a sensor group is a bundle of different field descriptions
Sensor Group example
- This is a virtual sensor 'engine', each engine has a certain amount of cylinders, and a certain amount of temperature sensors
- Each vehicle can have multiple engines
- In this example, our Car has two engines, Front-engine and Rear Engine
- Front-engine has 4 cylinders, and 1 telemetry sensor
- Rear-engine has 2 cylinders, and no telemetry sensor
{
"type": 666,
"num": 2,
"groups": [
{
"name": "cylinder",
"fields" : [
{"name": "flux", "unit": "milli-brown", "decPrecision": 0},
{"name": "Power", "unit": "watt", "decPrecision": 1}
]
},
{
"name": "telemetry",
"fields" : [
{"name": "Temperature", "unit": "C", "decPrecision": 1}
]
}
]
"properties": [
{
"id": "E1",
"name": "Front Engine",
"groups": [
[
{id: "C1", name: "Cylinder1"},
{id: "C2", name: "Cylinder2"},
{id: "C3", name: "Cylinder3"},
{id: "C4", name: "Cylinder4"}
],
[
{id: "T1", name: "Temperature1"}
]
]
},
{
"id": "E2",
"name": "Rear Engine",
"groups": [
[
{id: "C1", name: "Cylinder1"},
{id: "C2", name: "Cylinder2"}
],
[
]
]
}
]
}